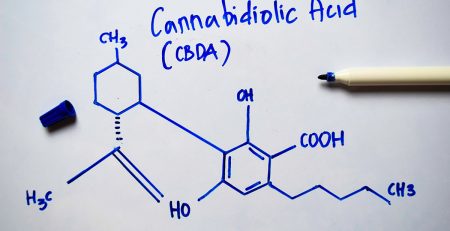
What are Cannabinoid Receptors?
Cannabinoid receptors are part of the endocannabinoid system. They impact many physical, mental, emotional and neurological processes in the body, as well as the brain. Researchers have discovered two main receptors CB1 and CB2 and believe they may have discovered a third one called CB3. These receptors respond to naturally-occurring endocannabinoids in our body and to CBD products that are consumed.
A useful analogy to understanding cannabinoid receptors, CBD and the endocannabinoid system is the lock and key concept. CBD acts like a key that unlocks CB1 and CB2 receptors which unleashes their beneficial impact on the endocannabinoid system. By doing this, the endocannabinoid system gets a boost in its ability to promote health and balance.
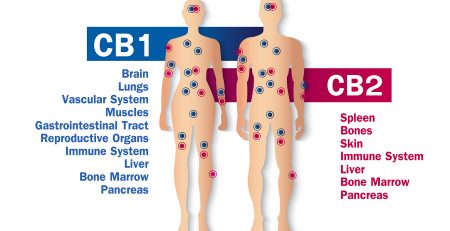
CB1 receptors are found in the brain, central nervous system and spinal cord. They are also in abundance throughout the thyroid, respiratory system, liver, endocrine gland and reproductive organs. CB1 and CB2 receptors are found in the eyes, cardiovascular system, gastrointestinal tract, pancreas, and bones. Science isn’t quite sure where CB3 receptors are as of yet, but this may change soon.
These receptors play an important role in the regulation of mood and pain. They also possess powerful anti-inflammatory properties for conditions including Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, cancer, depression, post-traumatic stress disorder, and other autoimmune disorders. CB1 and CB2 also play a key role in gut health.
Although much is currently known about cannabinoid receptors, more research is needed, especially to discover the locations and benefits of CB3. The puzzle pieces of receptors, cannabinoids (CBD), and the endocannabinoid system will come together with more research. One day hopefully soon, a clearer picture will be available to fully understand their benefits.